Spinal Cord Biology Diagrams Learn about the spinal cord, a tube of tissue that carries nerve signals from your brain to the rest of your body and back. Find out how it works, where it's located, what nerves are in it and what conditions can affect it.
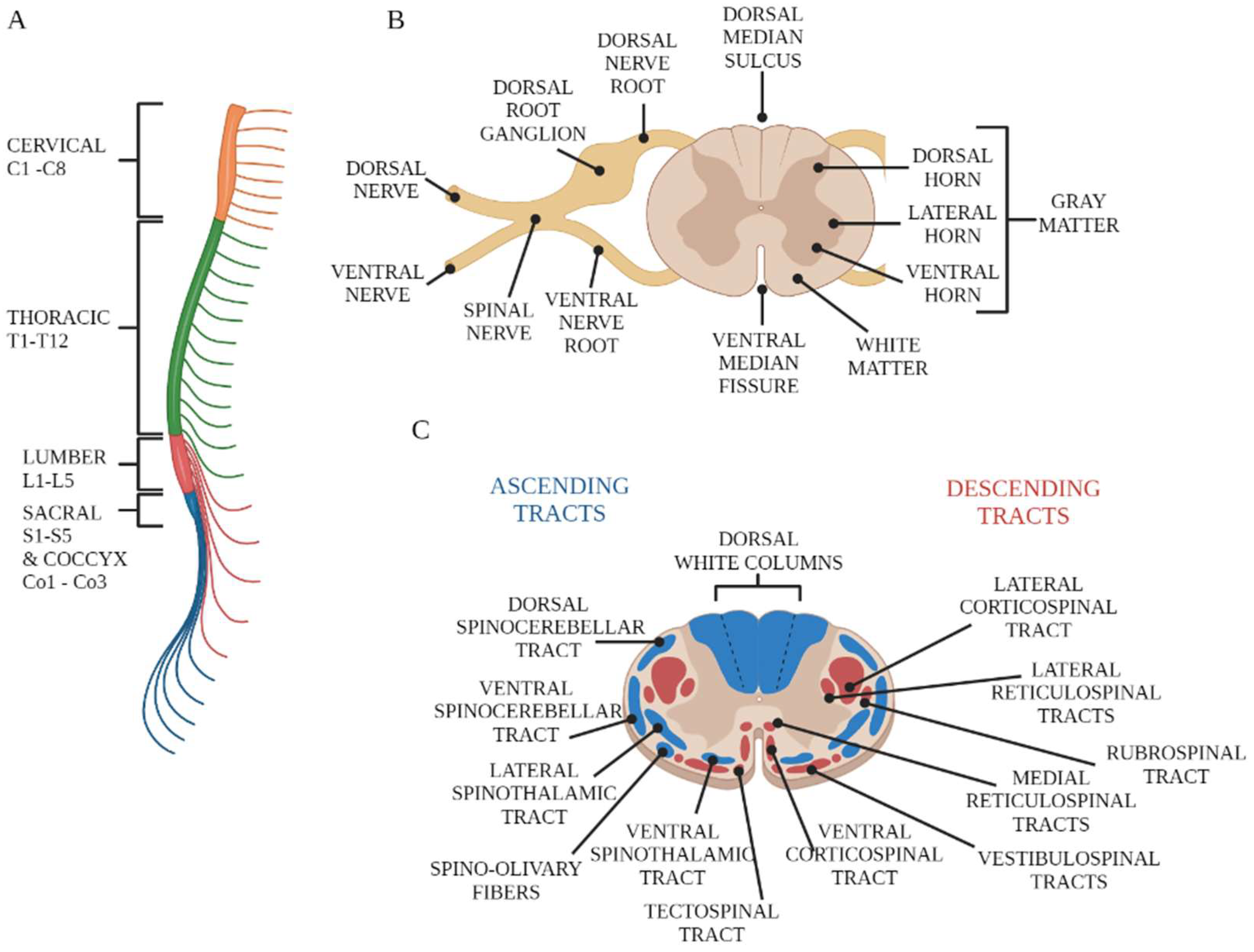
The spinal cord is a tubular structure composed of nervous tissue that extends from the brainstem and continues distally before tapering at the lower thoracic/upper lumbar region as the conus medullaris. The spinal cord is anchored distally by the filum terminale, a fibrous extension of the pia mater anchoring the spinal cord to the coccyx.[1] Protecting the spinal cord is the surrounding Learn about the spinal cord, a part of the central nervous system that conveys information between the brain and the body. Explore its segments, nerves, meninges, blood supply, and tracts with diagrams, videos, quizzes and more.

Spinal cord: Anatomy, structure, tracts and function Biology Diagrams
Learn about the spinal cord's structure, location, and role in carrying signals between the brain and the body. Find out how spinal cord injuries can affect movement and sensation and what treatments are available. Learn about the spinal cord, a tubular bundle of nervous tissue that connects the brain and the peripheral nervous system. Explore its structure, membranous coverings, blood supply, and clinical relevance.

Learn about the spinal cord, a long, cylindrical structure that transmits information between the brain and the body. Find out its location, regions, meninges, internal structure, spinal nerves, and clinical relevance.

Spinal Cord: Anatomy, Function & Structure Biology Diagrams
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system (CNS), which extends caudally and is protected by the bony structures of the vertebral column. It is covered by the three membranes of the CNS, i.e., the dura mater, arachnoid and the innermost pia mater. In most adult mammals it occupies only the upper two-thirds of the vertebral canal as the growth of the bones composing the vertebral
